The best ways to train a dog to stop barking
Types of Positive Reinforcement
Good rewards go far beyond food treats. Many different rewards work, depending on what each animal likes best. These can include happy words, gentle petting, favorite toys, or access to special places. Finding what truly motivates each animal makes training much more effective. Watching how animals react helps pick the best rewards for them.
Different animals prefer different rewards. While food might excite a dog, a cat might prefer playtime or a good scratching post. Understanding these differences leads to better results. Using various reward types creates more complete and successful training.
Consistency and Timing in Reinforcement
Being consistent with rewards helps animals learn faster. Changing your approach confuses animals and makes training less effective. Regular rewards help animals connect behaviors with good outcomes. Keeping rewards predictable and regular is essential for success. This helps animals clearly understand which actions bring rewards.
Giving rewards at the right time matters greatly. The reward should come right after the good behavior. This quick reward strengthens the connection in the animal's mind. The faster the reward comes, the stronger the animal remembers the connection. Immediate rewards help animals know exactly which behavior earned the reward.
Addressing Challenges in Positive Reinforcement
While positive methods work well, they sometimes present challenges. One common difficulty is knowing exactly which behavior to reward. Often, complex behaviors need breaking into smaller steps. Clear definitions and careful observation help solve this.
Another challenge involves handling unwanted behaviors during training. Instead of punishment, try redirecting attention or offering alternatives. Guiding the animal to better behaviors works better than scolding bad ones. Understanding why behaviors happen leads to more effective and kinder solutions.
Benefits of Positive Reinforcement Training
Positive training offers benefits beyond teaching good behaviors. It builds stronger bonds between people and animals, increasing trust and cooperation. This positive connection leads to happier, healthier relationships. These methods also create longer-lasting results and help animals flourish.
Positive training proves more enjoyable for both animals and trainers. This happy environment encourages learning and makes training rewarding for everyone. The focus on encouragement and rewards makes training a positive experience for all involved.
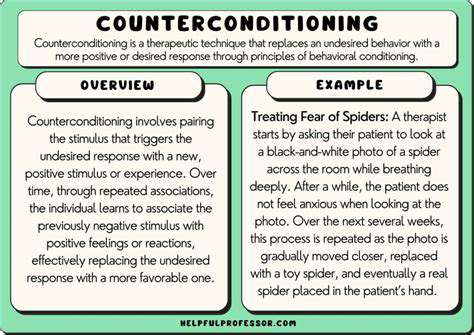
Desensitization and Counter-Conditioning
Desensitization: A Gradual Process
Desensitization, a key part of counter-conditioning, slowly introduces an animal to something scary while reducing fear responses. This careful process, often guided by experts, controls how much and how long the exposure lasts. The goal is to lessen fear over time, helping animals face challenging situations without panic. This step-by-step approach helps animals feel more in control of scary situations.
Desensitization usually starts by listing scary things from least to most frightening. Beginning with the easiest, animals gradually face scarier things while learning to stay calm. This controlled exposure lets animals confront fears safely.
Counter-Conditioning: Replacing Fear with Relaxation
Counter-conditioning replaces bad responses (like fear) with good ones (like calmness). This happens by pairing scary things with pleasant experiences that create calm feelings. By repeatedly connecting scary things with relaxation, animals learn to stay calm instead of fearful.
This process often uses relaxation methods like deep breathing or gentle massage. Combining gradual exposure with relaxation creates a powerful way to overcome fears.
Identifying the Feared Stimulus
The first important step is pinpointing exactly what causes fear. This requires careful observation of the animal's reactions to different situations. Knowing the exact cause of fear helps create the right treatment plan.
Developing a Hierarchy of Stimuli
A key part of desensitization involves creating a list of scary things from least to most frightening. This organized approach allows careful, controlled exposure to fears. Starting with easier items and moving to harder ones helps animals manage their fear better. This careful approach prevents overwhelming animals and helps them gain confidence gradually.
Techniques for Managing Anxiety
During desensitization, animals learn various relaxation methods to handle fear. These might include gentle massage, calming music, or quiet time. Learning these techniques gives animals tools to handle fear now and in the future.
The Role of a Therapist
Experienced trainers play a crucial role in desensitization. Their knowledge helps identify fears, create personalized plans, and provide support throughout training. They control how fast exposure happens, ensuring animals feel safe. They also track progress and adjust methods as needed for best results.
Professional Guidance and Support
Understanding the Root Cause of Barking
Finding out why your dog barks is essential for proper training. Is it from excitement, fear, boredom, or something else? Dogs barking at squirrels might need distraction, while door-barkers might need confidence building.
Watching your dog's body language and environment helps discover the real cause. This understanding guides your training to solve the real problem, not just stop the barking.
Positive Reinforcement Techniques
Positive methods form the foundation of good dog training. Rewarding quiet moments works much better than punishment. Using treats, praise, or toys as rewards teaches dogs that quiet brings good things. Being consistent strengthens this connection in your dog's mind.
Positive training builds good associations with desired behaviors, making learning enjoyable for both dog and owner.
Desensitization and Counter-Conditioning
For fear-based barking, gradual exposure to triggers paired with positive experiences helps change emotional responses. Start with mild triggers and slowly increase intensity, always pairing with something pleasant.
Environmental Management
Your dog's surroundings greatly affect behavior. Reducing triggers like loud noises or too much stimulation can help. Creating a calm, predictable environment often decreases barking.
Consistency and Patience
Training takes time and regular effort. Be patient - progress happens gradually. Short, frequent training sessions work better than long, irregular ones. Staying consistent with rewards helps your dog understand what you want.
Remember, each dog learns differently. Celebrating small successes and staying positive helps training succeed.
Seeking Professional Guidance
If barking problems continue, consider professional help. Expert trainers can assess the situation, find underlying issues, and create customized solutions. They provide valuable knowledge and personalized approaches to solve barking problems effectively.
Professional help saves time, reduces frustration, and builds better relationships between dogs and owners.