A complete guide to dog vaccination schedules
Outline
Core vaccinations provide vital defense against deadly canine illnesses like rabies and parvovirus.
Booster doses sustain protective immunity following initial vaccine protocols.
Lifestyle-specific vaccines address environmental exposure risks.
Customized vaccine plans require professional veterinary assessment.
Post-vaccine observation helps detect uncommon responses promptly.
Regular guideline reviews optimize disease prevention strategies.
Why Vaccinations Are Essential for Your Dog
The Importance of Core Vaccinations
Core immunizations form the foundation of canine disease prevention. These mandatory protections guard against rabies - a zoonotic killer with 100% fatality rates - along with highly contagious threats like parvovirus that can destroy a puppy's intestinal lining within 48 hours. Veterinary data shows unvaccinated dogs face 85% mortality rates when exposed to distemper.
Puppy vaccination sequences begin at 6-8 weeks, creating immunological memory through spaced doses. The American Animal Hospital Association emphasizes this phased approach allows immature immune systems to develop robust, lasting defenses. Missing booster windows during this critical period leaves puppies dangerously vulnerable.
Strategic Booster Timing and Risk Assessment
Immunity reinforcement through boosters works like insurance renewals - skipping them nullifies coverage. While core vaccines typically need triennial renewal, regional factors dramatically influence needs. Dogs in raccoon-heavy areas may require annual rabies boosters, whereas urban pets might follow extended schedules.
Lifestyle vaccines demand careful cost-benefit analysis. Active hunting dogs in wetland regions face 73% higher leptospirosis exposure compared to apartment pets, justifying extra protection. Conversely, homebody dogs may safely omit kennel cough vaccines unless boarding requirements arise.
Core vs. Non-Core Vaccines
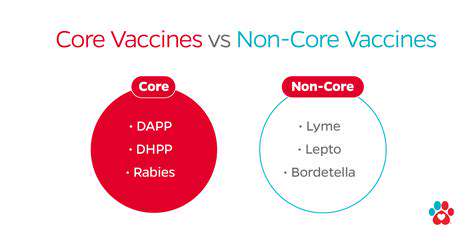
Mandatory Disease Shields
Core vaccines combat universal threats through legally enforced protocols. Rabies prevention alone saves approximately 59,000 human lives annually worldwide. Modern combination vaccines efficiently protect against multiple pathogens - a single injection often covers distemper, adenovirus, and parvovirus.
Customizable Protection Layers
Optional vaccines function like climate-specific clothing - essential for some, unnecessary for others. Lyme disease prevalence maps show 89% of cases cluster in Northeast and Midwest states, making the vaccine critical for dogs in these regions. Similarly, canine influenza shots become prudent during local outbreaks.
- Assess local disease prevalence through veterinary health alerts
- Calculate exposure risks from grooming/boarding frequency
- Factor in travel plans to endemic areas
Personalized Immunization Planning
Veterinary consults transform generic schedules into precision healthcare. Puppies with immune disorders might receive delayed/modified sequences, while working dogs often need accelerated protocols. Digital vaccine trackers now simplify record-keeping, sending automatic renewal reminders.
Post-Vaccination Vigilance
While 92% of dogs experience no side effects, monitoring remains crucial. Normal responses include temporary lethargy (12-24 hours) or mild injection-site warmth. Seek immediate care for facial swelling, vomiting, or difficulty breathing - these rare anaphylactic signs typically emerge within 30 minutes.
Typical Vaccination Schedule for Puppies
Developmental Immunization Phases
Puppies inherit temporary maternal antibodies that paradoxically interfere with early vaccines. This biological reality dictates the 6-16 week vaccination series - gradual exposure trains the immune system as maternal protection wanes. Missing even one appointment risks creating vulnerability windows.
Environmental Risk Adjustments
Urban puppies encountering elevator buttons and sidewalk germs may need earlier leptospirosis vaccines compared to rural littermates. Veterinarians increasingly use ZIP code disease data to customize schedules, potentially adding parasite prevention alongside core vaccines.
Vaccination Schedule for Adult Dogs
Maintenance Immunization Strategies
Titer testing now allows some dogs to extend booster intervals beyond traditional timelines. However, rabies laws remain strict - most states mandate 1-3 year revaccination regardless of antibody levels. Service dogs with public access requirements often follow maximized protection schedules.
Senior Dog Considerations
Aging immune systems (12+ years) may respond differently to vaccines. Some veterinarians recommend alternating core vaccines annually rather than combined administration. Semi-annual wellness checks help balance protection needs with age-related health changes.
- Essential fall care tips for your dog’s health
- Essential Needs for Your Dog's Health and Happiness
- Preventing Canine Heatstroke: Recognizing Symptoms in Dogs
- Early Detection of Dog Allergies: Key Signs for a Healthier Pet
- Canine Gestation Period: Understanding the 63 Day Timeline
- The Importance of Regular Veterinary Check Ups for Your Pets' Health
- Effective Strategies for Managing Allergies in Dogs
- Caring for senior dogs: A comprehensive guide
- How to protect your dog from fleas and ticks
- Dog gastrointestinal health: Prevention and care
- When and why your dog needs vaccinations
- How to recognize eye infections in dogs