How to improve communication with your dog
Index
Recognizing dog body language enhances communication and understanding.
Tail position indicates different emotions like happiness or fear.
Facial expressions and eye contact reveal a dog’s feelings.
Ears and body stiffness reflect a dog's emotional state.
Context is crucial for interpreting canine body language accurately.
Consistent vocal cues improve dog training and understanding.
Non-verbal signals enhance communication between dogs and owners.
Monitoring training progress is vital for effective communication.
Positive reinforcement encourages desired behaviors in dogs.
Engaging playtime fosters a strong bond and communication.
Establishing clear boundaries enhances understanding in dog training.
Tailoring rewards based on dog preferences boosts training success.
Addressing training challenges requires patience and positive strategies.
Recognizing Canine Body Language
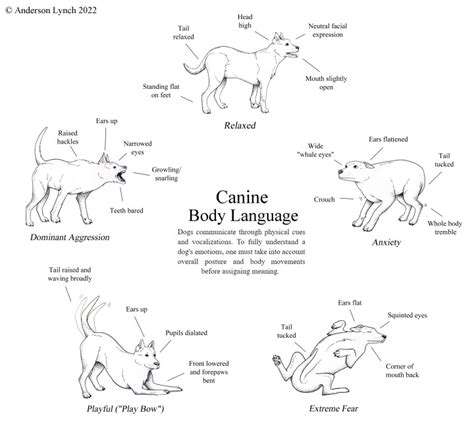
Understanding Basic Canine Postures
Our furry friends express volumes through their physical stance. A relaxed dog with upright posture and gentle tail movements typically shows confidence and satisfaction. Mastering these fundamental positions forms the foundation for decoding your pet's emotional state.
When a canine lowers its body or hides its tail, it might be experiencing nervousness or trying to appear non-threatening. Visible tension through raised fur or rigid appendages could suggest discomfort or alertness. Adapting your behavior based on these observations can dramatically enhance your interspecies connection.
The Role of Tail Position
Canine caudal communication offers vital emotional insights. An elevated, swaying tail usually reflects joy or anticipation, whereas a tail clamped beneath the body frequently demonstrates apprehension. Deciphering these caudal cues enables more precise emotional assessments.
Movement tempo adds another layer of meaning - hesitant wags might indicate uncertainty while rapid oscillations often show eagerness. Noticing these subtle differences improves interspecies dialogue and strengthens your relationship.
Facial Expressions and Eye Contact
Our companions convey emotions through facial movements much like people do. Relaxed facial muscles and gentle ocular expressions typically denote contentment, whereas tightened features may suggest discomfort. The American Kennel Club offers excellent visual references for these expressions.
Ocular engagement carries significant weight - sustained staring might be interpreted as confrontational, while soft glances demonstrate trust. Observing both facial movements and visual engagement patterns provides deeper insight into your pet's mindset.
Reading Ears and Other Body Parts
- Forward-pointing ears signal focused attention
- Flattened ears suggest nervousness
- Rigid musculature may indicate defensive posturing
Auricular positioning serves as real-time emotional indicators. Perked ears demonstrate curiosity, while retracted ears reveal submission. Fluency in these signals dramatically improves human-canine interaction.
Additional physical cues like weight distribution and limb positioning provide supplementary context. A shifting stance or evasive maneuvers often betray underlying anxiety.
The Importance of Context in Interpretation
Environmental factors critically influence behavioral analysis. While tail wagging during play signifies enjoyment, identical movements in confined spaces might signal distress. Comprehensive situational awareness remains essential for accurate interpretation.
External elements like unfamiliar animals or people can alter signal meaning. Always evaluate circumstances thoroughly before responding to perceived emotional displays.
Practical Applications: Improving Communication
Enhancing interspecies understanding requires responsive engagement with physical cues. Noticing patterns across different situations builds experiential knowledge. Cultivating calm atmospheres during stressful moments promotes clearer communication through reduced anxiety.
Regular, observation-based training sessions deepen mutual comprehension. Reward-based methods particularly strengthen relational bonds, ultimately creating attunement to your companion's needs and feelings.
Using Vocal Cues Effectively

Understanding Vocal Cues
Canines demonstrate remarkable responsiveness to vocal modulation. Articulation clarity and pitch variation significantly impact command effectiveness. Authoritative instructions benefit from firm delivery, while soothing tones work best for reassurance. Neuroscience confirms dogs process emotional inflections similarly to humans, making vocal quality paramount.
Verbal signals extend beyond direct commands. Specific sounds trigger particular reactions - higher frequencies often capture attention during interactive sessions. Approximately three-quarters of pet owners report their dogs prioritize tonal patterns over lexical content.
Establishing a Consistent Vocabulary
Effective communication requires linguistic consistency. Using identical terminology for specific actions reinforces neural pathways. Mixed phrases like alternating between sit and sit down create confusion and delay response times.
- Maintain single-word commands
- Begin training in low-distraction environments
- Progressively introduce complex settings
Incorporating Non-Verbal Signals
Physical gestures complement auditory commands effectively. Canines naturally interpret body language, making combined approaches particularly powerful. A raised palm accompanying stay reinforces the command through multiple sensory channels. This multimodal strategy accelerates comprehension and compliance.
Monitoring Your Progress
Tracking training efficacy through journaling reveals patterns and improvement areas. If commands prove ineffective, consider adjusting delivery style or reward timing. Regular assessment and adaptation optimize communication effectiveness and deepen mutual understanding.
Engaging in Consistent Training
Understanding Your Dog's Communication Signals
Canine communication blends physical, vocal, and contextual elements. Tail movements require situational interpretation - vigorous wagging suggests excitement while stiff, slow motions may indicate tension. Research confirms dogs interpret human emotional states through facial cues, making mutual observation crucial for relationship building.
Setting a Training Routine
Regular practice sessions enhance learning retention. Optimal training involves brief 5-10 minute intervals multiple times daily. Incorporating diverse commands maintains engagement and stimulates cognitive development beyond basic obedience.
Utilizing Positive Reinforcement
Reward-based training leverages natural learning mechanisms. Immediate treat distribution or praise following desired actions strengthens behavioral patterns. Veterinary studies confirm positive methods increase voluntary compliance and trust.
Incorporating Play into Training
Interactive games like fetch or puzzle toys merge education with enjoyment. Varied activities reduce stress while reinforcing commands, creating positive associations with learning processes.
Establishing Clear Boundaries
Consistent rule enforcement prevents confusion. Unified household standards regarding permitted behaviors help canines understand expectations, reducing anxiety and frustration.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Techniques
Regular skill assessments identify strengths and improvement areas. Flexible methodology adaptation ensures personalized training approaches that respect individual learning styles.
Establishing a Strong Bond
Understanding Canine Body Language
Interpreting physical cues remains fundamental for relationship building. Tail position and ear orientation provide real-time emotional updates. Research confirms dogs differentiate human emotional expressions, making mindful interaction essential.
Consistent Training Practices
Standardized command language across family members prevents confusion. Integrating training into daily routines through walk-based exercises enhances focus and cooperation.
Engaging in Interactive Activities
Shared challenges like agility courses or scent games strengthen relational ties through collaborative problem-solving. These experiences create positive associations while stimulating mental acuity.
Utilizing Positive Reinforcement

Understanding the Basics of Positive Reinforcement
Reward-based training leverages behavioral psychology principles. Immediate treat distribution following desired actions creates strong behavior-reward associations. This method proves more effective than punitive approaches according to comparative animal studies.
The Importance of Consistency
- Uniform household standards prevent confusion
- Regular practice sessions enhance retention
- Clear expectations facilitate faster learning
Choosing the Right Rewards
Individual motivation varies - some dogs prefer play rewards over food incentives. Identifying high-value motivators through experimentation optimizes training effectiveness. Immediate reinforcement timing remains critical for cognitive association.
Addressing Challenges in Training
Persistent issues require creative solutions like teaching incompatible behaviors. Clicker training provides clear feedback markers, while patience ensures gradual improvement. Celebrating incremental successes maintains positive momentum throughout the training journey.
- Smart Technology Revolutionizing Daily Living and Industry Practices
- The Unique Temperament of Every Dog: A Guide for Dog Owners
- Decoding Canine Behavior: A Comprehensive Guide
- Essential Needs for Your Dog's Health and Happiness
- The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Developing Effective Communication Skills
- Effective Strategies to Calm a Stressed Dog
- Decoding Your Dog's Body Language for Better Communication
- Effective Ways to Manage Separation Anxiety in Dogs
- How to reduce separation anxiety in dogs
- Preventing accidents during outdoor dog activities
- Simple ways to reduce stress in dogs
- How to build better relationships between dogs