How to spot nutritional deficiencies in dogs
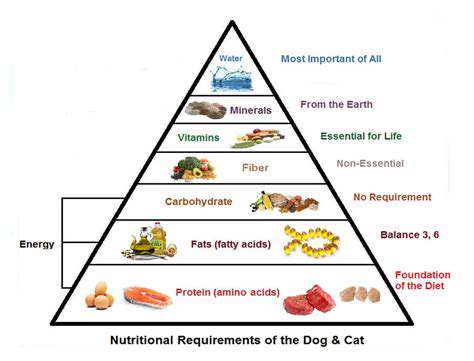
Protein is crucial for dogs, serving as the fundamental building block for their muscles, organs, skin, and coat. Adequate protein intake is essential for healthy growth and development in puppies and maintaining muscle mass and overall well-being in adult dogs. A deficiency in protein can lead to muscle wasting, weakened immune function, and a compromised ability to heal from injuries. Understanding the specific protein needs of your dog, based on their age, breed, activity level, and overall health, is vital for ensuring optimal nutrition.
High-quality protein sources, such as lean meats, poultry, and fish, are preferable. These provide essential amino acids that your dog's body needs but cannot produce on its own. Ensure that the protein source in your dog's food is easily digestible to maximize its nutritional benefits.
Essential Fatty Acids: Supporting Skin and Coat Health
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are vital for maintaining a healthy skin and coat. These essential fats play a crucial role in skin barrier function, reducing dryness and flakiness. A deficiency can manifest as dull, dry, or brittle hair and skin conditions. These fatty acids are also important for brain function and overall well-being, particularly in puppies.
Vitamins: Supporting Various Bodily Functions
Vitamins are crucial for a wide range of bodily functions in dogs, including immune function, cell growth, and energy production. Vitamin A, for example, is essential for healthy vision and skin, while vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that supports the immune system. Deficiencies in these vitamins can result in various health problems, from impaired vision to weakened immune responses.
A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, and supplements can help ensure your dog receives the necessary vitamins. Consult with your veterinarian to determine if your dog requires any specific vitamin supplements based on their individual needs.
Minerals: Crucial for Bone Health and Function
Minerals are essential for various bodily functions, including bone health, muscle function, and nerve transmission. Calcium and phosphorus, for example, are vital for strong bones and teeth. Iron is needed for oxygen transport, while zinc is essential for immune function and wound healing. A deficiency in any of these minerals can lead to a variety of health problems, such as weakened bones, poor wound healing, and lethargy.
Hydration: Maintaining Overall Health
Water is arguably the most essential nutrient for any living organism, including dogs. It's crucial for regulating body temperature, transporting nutrients, and eliminating waste products. Dehydration can lead to a range of health problems, including kidney failure, lethargy, and even death. Ensure that fresh water is always available for your dog, and encourage them to drink regularly, especially during hot weather or after strenuous exercise.
Fiber: Supporting Digestive Health
Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy digestion in dogs. It aids in the movement of food through the digestive tract, preventing constipation and promoting regularity. A diet lacking in fiber can lead to digestive issues, such as diarrhea or constipation. Properly sourced fiber, such as that found in fruits and vegetables, is essential for a healthy digestive system. Consider the overall nutritional profile of the food you provide your dog to ensure appropriate fiber content.
Mindfulness is the practice of being fully present and engaged in the moment without judgment. It involves observing your thoughts and feelings without getting caught up in them. This awareness can lead to deeper self-understanding and a greater appreciation for life's experiences.
Dietary Considerations and Your Dog's Specific Needs
Dietary Considerations and Your Dog's Health
A dog's diet is crucial for its overall health and well-being. Proper nutrition provides the necessary energy, nutrients, and building blocks for growth, development, and maintenance of optimal physical condition. A balanced diet tailored to a dog's specific needs, age, and activity level is essential for preventing various health problems.
Choosing the right food can significantly impact your dog's health and longevity. Poor dietary choices can lead to weight issues, digestive problems, allergies, and even more serious health conditions. Understanding the nutritional requirements of your dog is key to providing them with the best possible care.
Understanding Your Dog's Nutritional Needs
Different breeds, sizes, and ages of dogs have varying nutritional needs. A puppy, for example, requires a diet rich in protein and essential nutrients for healthy growth and development. Adult dogs need a balanced diet to maintain their overall health and energy levels, while senior dogs may require specific formulas to support aging joints and other bodily functions.
Factors such as activity levels also influence dietary needs. An extremely active dog will need more calories and nutrients compared to a dog with a more sedentary lifestyle. Consider your dog's daily activity when choosing food and portion sizes.
Common Dietary Issues in Dogs
Obesity is a prevalent issue in dogs, often stemming from overfeeding and a lack of exercise. Obesity can lead to various health complications, including joint problems, heart disease, and diabetes. Monitoring your dog's weight and adjusting their food intake accordingly is crucial to prevent obesity.
Food allergies and intolerances are another significant concern. Symptoms such as itching, skin rashes, vomiting, and diarrhea can indicate an allergy or intolerance. Identifying the specific triggers through dietary trials and consulting with your veterinarian is essential for managing these issues.
The Importance of Gradual Dietary Changes
Sudden changes in a dog's diet can disrupt their digestive system and lead to discomfort or illness. Introducing new foods gradually is crucial for avoiding stomach upset and ensuring a smooth transition. Gradually incorporating new food into their current diet over a period of 7-10 days can minimize any digestive distress.
The Role of Veterinary Guidance
Consulting your veterinarian is always recommended for personalized dietary advice. Your veterinarian can assess your dog's specific needs and recommend a suitable diet based on their breed, age, health condition, and activity level. They can also provide guidance on portion sizes and address any dietary concerns or allergies.
Veterinarians are well-versed in the latest nutritional research and can provide expert recommendations for maintaining your dog's health and well-being through appropriate dietary choices.