Rising Sea Levels: The Impacts on Coastal Communities and Ecosystems
The Causes Behind Rising Sea Levels
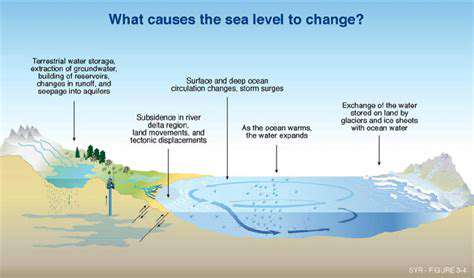
The Role of Climate Change
Climate change is a significant driver of rising sea levels, primarily due to the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. As temperatures increase, ice masses that have existed for millennia are rapidly diminishing. This process contributes directly to rising water levels in the oceans.
Additionally, the thermal expansion of seawater due to higher temperatures is another factor exacerbating this problem. When water heats up, it expands, leading to a further increase in sea levels.
The repercussions of these changes are not confined to distant oceans; they have direct consequences for coastal communities around the world. Community planners and policymakers must adapt to these evolving conditions to safeguard infrastructure and public health.
Moreover, changes in precipitation patterns, increased frequency of storms, and flooding events are anticipated as a result of climate change. These factors can lead to compounded risks for areas that are already vulnerable to sea-level rise.
Efforts to mitigate climate change can play a critical role in slowing the rise of sea levels, emphasizing the importance of global cooperation and environmental policies.
The Impact on Coastal Ecosystems
Coastal ecosystems, such as mangroves, salt marshes, and coral reefs, are particularly susceptible to the effects of rising sea levels. These environments serve as vital buffers against storm surges and harbor immense biodiversity, making their protection crucial.
Increased salinity from encroaching saltwater can harm freshwater supplies and disrupt the delicate balance of coastal habitats. The stress on these ecosystems can lead to loss of species and decreased resilience against environmental changes.
Furthermore, as sea levels rise, it can lead to habitat loss for both terrestrial and aquatic species. Many animals rely on specific coastal conditions to thrive, and even slight changes can displace them.
Human activities, such as coastal development and pollution, further exacerbate the vulnerability of these ecosystems. Protecting and restoring natural habitats becomes increasingly important for maintaining biodiversity in the face of rising waters.
Conservation efforts, along with sustainable management practices, are essential to ensure the health of coastal ecosystems amid ongoing environmental challenges.
Impacts on Coastal Communities
Economic Consequences
Coastal communities often rely on industries such as fishing, tourism, and real estate. Rising sea levels threaten these economic pillars, leading to potential job losses and decreased income.
As coastal properties become more vulnerable to flooding, property values may decline, resulting in significant financial losses for homeowners and investors alike.
Insurance companies may raise premiums or refuse coverage altogether in high-risk areas, leaving residents financially exposed and unable to recover from storm damage.
The loss of beach access and marine resources can also deter tourists, leading to decreased revenue for local businesses that depend on this influx.
Local governments may face increased costs related to infrastructure repair and maintenance, putting further strain on municipal budgets and potentially leading to higher taxes for residents.
Social Impacts
Displacement resulting from rising sea levels can create significant social upheaval. Families may be forced to relocate, breaking community ties and disrupting social networks.
As communities become vulnerable, issues such as mental health difficulties can arise due to the stress of uncertainty and loss associated with climate change impacts.
Environmental injustice may also be exacerbated, as low-income and marginalized communities often bear the brunt of flooding and may lack the resources to adapt.
Community resources, such as schools and hospitals, may be compromised, impacting residents' quality of life and access to essential services.
Conversely, some communities may become more united in their efforts to adapt, leading to increased activism and collaborative initiatives focused on resilience and sustainability.
Environmental Consequences
Rising sea levels can lead to the inundation of wetlands, which serve as critical habitats for many species and act as natural barriers against storms.
Coastal ecosystems, such as mangroves and salt marshes, are at risk of degradation, which can result in a loss of biodiversity and disruption of food chains.
The salinization of freshwater resources due to rising tides threatens drinking water supplies and the viability of local agriculture.
Marine life, including fish and invertebrates, can be adversely affected as their habitats shift, potentially leading to declines in populations critical for both ecology and economy.
Additionally, coastal erosion can accelerate as sea levels rise, leading to further habitat loss and negatively impacting coastal communities’ natural protective barriers.
Adaptation Strategies
Communities facing rising sea levels can adopt various strategies to mitigate impacts, including constructing sea walls and levees to protect against flooding.
Restoring natural barriers such as wetlands and marshes not only protects shorelines but also enhances local ecosystems and biodiversity.
Implementing zoning laws and building regulations can help guide development away from the most vulnerable areas, reducing potential future damages.
Investing in community education and awareness programs can empower residents to understand risks and take preventative measures.
Collaborative efforts between governments, businesses, and non-profits can foster innovation in climate resilience strategies and funding opportunities.
Policy and Governance
The role of policy in addressing rising sea levels is crucial, as effective governance can facilitate proactive measures and adaptation strategies.
Local and national governments must come together to develop comprehensive plans that address both immediate threats and long-term sustainability.
Funding for infrastructure improvements and climate adaptation projects can be targeted toward the most at-risk communities to ensure equitable support.
Regulatory frameworks need to adapt to the changing climate, with policies reflecting the need for environmental protection and sustainable development.
Public engagement and transparency in decision-making processes can build trust and encourage community participation in governance related to climate impacts.
Environmental Consequences

Impact on Coastal Ecosystems
Rising sea levels pose a significant threat to coastal ecosystems, including mangroves, salt marshes, and coral reefs. These ecosystems provide essential services, such as habitat for wildlife and protection against storm surges. As water encroaches on land, many of these vital areas may become inundated, leading to loss of biodiversity. This loss can disrupt food chains and compromise the health of marine species. Such changes can have lasting effects on both the ecosystem and the local economy that depends on these resources.
Moreover, coastal flooding can lead to increased salinity in freshwater systems, affecting the growth and reproduction of plants and animals. This shift in water chemistry can severely impact species that rely on estuarine environments. It can also damage essential habitats for young fish, which depend on sheltered coastal areas for their development. As habitats shift or disappear, we may witness a decline in fish stocks and the communities that rely on them for livelihoods.
Coral reefs are particularly vulnerable to rising sea levels, as they require specific conditions to thrive. Elevated water levels can lead to increased sedimentation, which can smother corals and hinder their growth. Additionally, rising temperatures often accompany sea level rise, contributing to bleaching events that further harm these delicate ecosystems. The loss of coral reefs not only endangers marine species but also the tourism and fishing industries associated with them.
Salt marshes play a critical role in buffering coastal areas from wave action and erosion. With rising seas, these areas may migrate inland if there is adequate space. However, urban development often limits this migration, leading to significant habitat loss. The loss of these natural barriers increases the vulnerability of coastal communities to flooding and erosion.
Ultimately, the environmental consequences of rising sea levels extend far beyond coastal ecosystems, affecting everything from water quality to storm resilience. Effective management strategies and restoration efforts are crucial to mitigate these impacts. Without proactive measures, the ecological imbalance created by rising seas could have dire consequences for both nature and human society.
Socioeconomic Effects on Communities
The socioeconomic implications of rising sea levels are profound, particularly for coastal communities that rely on agriculture, fishing, and tourism. As land becomes submerged, livelihoods that depend on these sectors are threatened. Families may face economic hardships, and communities risk losing their cultural heritage tied to the land. Vulnerable populations may find it increasingly difficult to adapt to these changes, leading to social upheaval.
With limited resources, many coastal communities struggle to implement necessary changes to infrastructure. Increased flooding can damage homes and disrupt local businesses, creating a cycle of poverty that is hard to escape. As homes become uninhabitable, there is a growing need for relocation, which introduces further challenges related to displacement. This displacement can strain urban areas, leading to increased competition for resources and services.
Insurance costs are rising as properties in coastal areas face higher risks from flooding. Many homeowners may find their policies are no longer affordable or available. Consequently, this can deter potential new residents and investors, shrinking the economic base of these communities. Without adequate funding and support, local governments may struggle to develop effective adaptation strategies.
Tourism-dependent economies also face threats from rising sea levels. Beaches and recreational areas that attract visitors may erode and disappear, leading to significant revenue losses. As coastal attractions diminish, businesses may close or relocate, exacerbating unemployment in these areas. Local governments must prioritize investment in resilient infrastructure to protect their economies and communities.
In summary, the socioeconomic effects of rising sea levels require urgent attention and comprehensive planning. Collaborative efforts between local, state, and federal entities are essential for creating sustainable solutions. Addressing both the environmental and economic dimensions of this issue is crucial for the resilience of coastal communities.
Health Risks Linked to Rising Waters
As sea levels rise, coastal communities face increased health risks due to flooding and water contamination. Floodwaters can introduce pollutants and pathogens into drinking water supplies, leading to waterborne diseases. This can create serious public health crises, especially among vulnerable populations. Contaminated water can cause gastrointestinal illnesses and other serious health complications.
In addition to physical health risks, the psychological impact of climate-related displacement can be profound. Individuals who lose their homes or community connections may experience increased rates of anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. Access to mental health services may diminish as communities are uprooted, compounding these challenges.
Vector-borne diseases also pose an increasing threat in coastal regions impacted by rising sea levels. As ecosystems change, so too can the habitats for mosquitoes and other disease-carrying insects. This can lead to the spread of diseases such as malaria and dengue fever, putting more residents at risk. Public health systems must adapt to these evolving threats, requiring additional resources and training.
Heat-related illnesses may also increase as sea levels rise and populations become more concentrated in urban areas. Poorly planned urban development, combined with higher temperatures, can lead to heat islands that exacerbate heat-related health issues. Communities must invest in green infrastructure to aid in cooling efforts and enhance overall public health.
In conclusion, the health risks associated with rising sea levels are multifaceted and complex. Proactive health planning, community education, and resource allocation are critical to mitigating these risks. Integrating health considerations into urban planning is vital for ensuring the well-being of coastal populations.
Policy Responses and Adaptation Strategies
Addressing rising sea levels necessitates comprehensive policy responses and adaptation strategies. Governments need to collaborate with scientists and community leaders to understand the local implications of sea level rise. Effective policies must consider both immediate risks and long-term planning for sustainability. This includes investments in resilient infrastructure that can withstand flooding and other environmental stresses.
One promising strategy is the implementation of nature-based solutions, such as restoring wetlands and building artificial reefs. Such approaches not only protect against rising waters but also enhance biodiversity and mitigate erosion. Communities that invest in these natural defenses can bolster their ecosystems while reaping additional economic benefits.
Regulatory frameworks must also evolve to reflect the challenges posed by rising sea levels. Zoning laws should prioritize smart growth and carefully consider land use in vulnerable areas. Incentives for developers to build with resilience in mind can促进更安全、更可持续的社区未来。 These measures are essential for protecting both people and the environment.
Stakeholder engagement is crucial to developing effective adaptation strategies. Local communities possess unique insights into their challenges and needs. Including community voices in the decision-making process fosters ownership and ensures that policies resonate with those most affected by rising sea levels.
In summary, addressing rising sea levels requires a multifaceted approach that blends science, policy, and community engagement. Sustainable policies and adaptive strategies can enhance resilience, safeguard livelihoods, and protect vulnerable populations. To succeed, these efforts must be prioritized by all levels of government—a unified approach is essential for addressing this global challenge.
Technological Innovations in Mitigation
Technological innovations hold great potential for mitigating the impacts of rising sea levels on coastal communities. Advances in monitoring equipment can provide crucial data to assess changes in sea levels and predict future trends. These tools enable policymakers to make informed decisions based on accurate, real-time information. Moreover, they facilitate early warning systems that can alert communities about impending flooding.
Infrastructure advancements, such as flood barriers and sea walls, can protect vulnerable areas from encroaching waters. Innovations in materials and design can enhance the effectiveness and resilience of these structures. Additionally, the implementation of smart technology can help manage water flow and prevent flooding in urban settings.
Another promising area of innovation is in climate modeling and simulation. These technologies allow researchers to better understand and visualize the potential impacts of rising sea levels. By engaging in predictive modeling, communities can identify at-risk areas and prioritize mitigation efforts accordingly. This proactive approach can lead to more efficient resource allocation and planning.
Community engagement tools, including mobile applications and online platforms, can facilitate communication regarding adaptation strategies. These technologies empower citizens to report flooding events and engage in local decision-making. By fostering a sense of community ownership, these tools support collective resilience efforts.
In concluding, innovative technologies play an essential role in addressing the challenges posed by rising sea levels. Continued investment in research and development can yield solutions that not only protect coastal communities but also promote sustainable practices. Embracing technological advancements is a critical step in our global response to climate change.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
1. Coastal Protection Measures
Coastal protection measures are crucial in safeguarding communities against the threats posed by rising sea levels. These include the construction of seawalls, levees, and breakwaters designed to absorb and deflect wave energy. Such infrastructure can help prevent erosion and flooding, protecting valuable land and property.
Additionally, approaches like beach nourishment involve replenishing eroded shorelines with sand, which can create natural buffers against storm surges. This method, while effective, requires ongoing maintenance and can be costly over time, particularly in areas facing significant erosion.
Living shorelines, a more eco-friendly option, utilize natural elements such as marsh plants and oyster reefs to stabilize coastlines. These solutions enhance biodiversity and habitat resilience while simultaneously providing protection against sea-level rise.
As communities invest in these protective measures, it's essential to engage stakeholders in the planning process, ensuring that social, economic, and ecological factors are considered. This collaborative approach helps build public support and fosters a shared commitment to addressing sea-level rise.
Ultimately, the success of coastal protection measures will hinge on ongoing assessments of their effectiveness, especially as climate patterns change. Regular monitoring allows for adaptive management strategies to be implemented, ensuring these defenses remain robust against future challenges.
2. Community Engagement and Policy Development
Community engagement is vital in creating effective strategies to combat the impacts of rising sea levels. Local populations must be informed about the risks and involved in decision-making processes that affect their lives and environment. Educational initiatives can empower individuals to take action, from advocating for policy changes to implementing sustainable practices in their homes.
Encouraging public participation in the development of resiliency plans allows for more tailored solutions that reflect the unique needs of each coastal community. Effective engagement fosters a sense of ownership among residents, increasing the likelihood of successful implementation of adaptation strategies.
On the policy front, governments at both local and national levels must prioritize climate adaptation in planning and zoning regulations. Implementing policies that support sustainable land use and development will be crucial in minimizing vulnerability to sea-level rise. These regulations can help protect critical ecosystems and limit further encroachment into risky coastal areas.
In addition to local efforts, intergovernmental cooperation is essential to share resources and strategies across regional and national borders. Global challenges like climate change require collective responses, and collaborative policies can help address the impacts of rising sea levels more effectively.
Finally, ongoing research and data collection are critical to informing policy decisions. By understanding the latest science related to climate change and its effects on sea levels, communities can better anticipate changes and adjust their strategies to meet future challenges.