サプライチェーンにおける持続可能な廃棄物管理
Waste reduction strategies are no longer a niche environmental concern but a crucial component of sustainable development. Addressing waste at its source is paramount to minimizing the environmental impact of our consumption patterns. This involves a comprehensive approach that considers the entire lifecycle of products, from design and production to consumption and disposal. The goal is to create a circular economy where resources are reused and recycled, minimizing the need for virgin materials and the generation of waste.
Implementing effective waste reduction strategies requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes promoting the use of reusable products, encouraging responsible consumption, and supporting the development of innovative technologies for waste management. A shift in societal values, emphasizing mindful consumption and reducing our reliance on disposable items, is essential to achieving meaningful waste reduction outcomes.
The Economic Benefits of Waste Reduction
The economic benefits associated with waste reduction are significant and far-reaching. Reducing waste translates directly into savings on landfill disposal costs and resource extraction. Furthermore, the development of a circular economy fosters innovation and creates new economic opportunities in areas like recycling, reuse, and the development of sustainable products.
Waste reduction initiatives can stimulate job creation in related industries, from recycling facilities to product design and manufacturing. These initiatives also promote a more resilient and sustainable economy, less susceptible to fluctuations in resource prices and environmental damage.
Technological Advancements in Waste Management
Technological advancements are transforming waste management, offering innovative solutions for waste reduction. From advanced sorting technologies that improve recycling rates to innovative bio-based materials that reduce reliance on traditional plastics, there are numerous possibilities.
The rise of advanced technologies is driving efficiency and cost-effectiveness in waste management. These improvements not only contribute to minimizing environmental impact but also offer significant economic advantages. This includes the development of advanced materials and processes for waste transformation and reuse.
Policy and Public Awareness Initiatives
Effective waste reduction requires a concerted effort from both policymakers and the public. Government policies can drive change by incentivizing sustainable practices, mandating stricter regulations on waste disposal, and promoting investments in waste management infrastructure.
Public awareness campaigns are crucial in educating consumers about the importance of waste reduction and encouraging responsible consumption habits. Raising public awareness is essential in fostering a culture of environmental consciousness and motivating individuals to make sustainable choices in their daily lives. These campaigns can highlight the environmental and economic benefits of responsible waste disposal.
Implementing Circular Economy Principles in Supply Chain Design
Understanding Circular Economy Principles
Circular economy principles fundamentally shift the linear take-make-dispose model of production and consumption towards a closed-loop system. This involves designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. Core tenets include resource efficiency, material reuse, and renewable energy sources. Implementing these principles requires a significant shift in mindset, moving from a focus on extracting resources to optimizing resource utilization and minimizing environmental impact throughout the entire supply chain.
A key aspect of this transition is recognizing the value embedded in waste. Instead of discarding materials, circular economy principles encourage their recovery, reuse, and repurposing, thereby reducing reliance on virgin resources and minimizing waste generation.
Designing for Disassembly and Material Recovery
Designing products for easy disassembly and material recovery is crucial for circular supply chains. This involves considering the entire lifecycle of the product, from initial design to eventual end-of-life management. Employing modular designs, standardized interfaces, and readily accessible components enables efficient dismantling and the separation of different materials for reuse or recycling.
Using readily recyclable materials in the product design is also vital. Products should be made from materials that can be easily processed and recycled without significant loss of quality or value. This minimizes the need for complex and expensive sorting processes.
Optimizing Material Flow and Logistics
Efficient material flow and logistics are essential for minimizing transportation costs and environmental impact. Implementing strategies such as closed-loop logistics systems, optimizing transportation routes, and utilizing shared transportation networks can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of the supply chain. This includes considering the transportation of materials from production to consumption, and back to the production facilities for reuse or recycling.
Collaboration among supply chain partners is vital for establishing effective material flow systems. Jointly developing and implementing strategies for material recovery and reuse can create a more sustainable and resilient supply chain.
Promoting Collaboration and Partnerships
Circular economy implementation requires strong collaboration among various stakeholders throughout the supply chain, including manufacturers, retailers, consumers, and waste management companies. By fostering partnerships and information sharing, companies can develop innovative solutions for material recovery, reuse, and recycling.
This collaborative approach can also extend to the development of new business models that encourage product reuse and repair, creating opportunities for innovation and economic growth. Partnerships can drive the development of innovative circular solutions.
Implementing Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Implementing Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) policies holds manufacturers accountable for the end-of-life management of their products. This approach encourages manufacturers to design products with recyclability and reusability in mind, reducing waste and pollution. EPR policies can incentivize the development of innovative recycling technologies and encourage the use of sustainable materials.
EPR policies can also encourage product take-back programs, which allow consumers to return used products for recycling or reuse, closing the loop and reducing the environmental impact of waste.
Enhancing Product Durability and Lifespan
Designing for durability and longevity extends the lifespan of products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste generation. This involves using high-quality materials, employing robust manufacturing processes, and building in maintenance and repair capabilities. By building products to last longer, companies can significantly reduce the demand for new products and therefore the impact on the environment.
Encouraging Consumer Engagement and Education
Consumer engagement and education play a critical role in driving the adoption of circular economy principles. Educating consumers about the benefits of product reuse, repair, and recycling encourages responsible consumption habits. Promoting initiatives that support product reuse and repair services, such as repair cafes, can empower consumers and encourage a shift towards more sustainable choices.
Clear and accessible information about product lifecycle and recycling options empowers consumers to make informed decisions, contributing to the overall success of circular economy initiatives.
Waste Reduction Strategies Across the Supply Chain
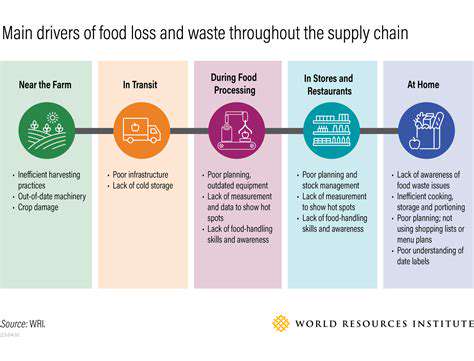
Waste Reduction Strategies in the Home
Implementing waste reduction strategies at home is crucial for minimizing environmental impact. Small changes in daily habits can significantly reduce the amount of waste generated. This includes choosing reusable alternatives to single-use plastics, like water bottles and shopping bags. Proper waste sorting and composting food scraps are also effective ways to divert waste from landfills and promote sustainability.
Recycling programs, while valuable, often have limitations. It's important to understand the local guidelines and participate actively in appropriate recycling processes. By learning about what materials are recyclable in your area, you can effectively contribute to waste diversion and resource conservation.
Industrial Waste Management Solutions
Large-scale industries generate substantial amounts of waste, requiring specialized waste management strategies. Implementing innovative solutions is vital for minimizing the environmental footprint of manufacturing processes. Strategies such as material substitution, waste-to-energy technologies, and improved process design can significantly reduce the volume of hazardous and non-hazardous waste produced. Waste reduction is a crucial consideration in many industrial settings.
Efficient recycling and recovery processes are essential for sustainable operations. These processes ensure that valuable materials are salvaged and reused, reducing the need for raw materials and minimizing the environmental strain on resources.
Waste Reduction in Municipal Areas
Municipalities play a critical role in promoting waste reduction strategies. Raising public awareness about the importance of waste reduction is crucial for encouraging individual and community-wide action. Implementing comprehensive waste management plans that include education campaigns, improved infrastructure, and incentives for waste reduction can yield positive results.
Investing in recycling and composting facilities can effectively divert waste from landfills. These facilities provide infrastructure for processing recyclable materials and creating compost from organic waste, reducing the environmental impact and conserving valuable resources.
Composting and its Benefits
Composting is a simple yet effective method for reducing organic waste. It converts food scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials into nutrient-rich compost, which can then be used to enrich garden soil. Composting reduces landfill waste and promotes soil health, leading to a more sustainable environment.
Composting reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, promoting natural soil health. This natural approach to gardening is essential for creating a healthier ecosystem. It's a simple way to contribute to a more sustainable environment, reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers and promoting natural processes.
Sustainable Packaging Innovations
The packaging industry is increasingly focusing on sustainable alternatives to traditional materials. The development of biodegradable and compostable packaging materials is crucial for reducing plastic pollution. These innovative materials offer a promising pathway towards minimizing the environmental impact of packaging. The use of recycled materials in packaging is also gaining traction, promoting resource conservation.
Innovative designs for packaging can reduce the overall amount of material needed. Minimizing material usage is essential for reducing waste and environmental impact. Reducing the size and weight of packaging can significantly lower transportation costs and energy consumption, contributing to a more sustainable supply chain.
Waste Reduction through Consumer Awareness
Consumer awareness plays a significant role in waste reduction efforts. Educating consumers about the environmental consequences of waste generation is critical for promoting responsible consumption patterns. Choosing products with minimal packaging, opting for reusable items, and actively participating in recycling programs are all important steps. Encouraging consumers to make conscious choices about the products they purchase and the waste they generate is essential for a sustainable future.
Understanding the life cycle of products and the impact of consumption habits are vital for informed decision-making. Consumers can make a difference by supporting companies that prioritize sustainability and reducing their environmental impact through their purchasing decisions.
Collaboration and Transparency for Supply Chain Sustainability
Fostering a Culture of Collaboration
A truly effective team relies on open communication and collaboration. This shared understanding and commitment to working together fosters innovation and problem-solving. Open-door policies and regular team meetings are crucial for facilitating interaction and allowing every member to contribute meaningfully. Encouraging the exchange of ideas and perspectives, even those that differ from the majority opinion, is essential for creative problem-solving. Constructive criticism and active listening are paramount in collaborative environments.
Transparency is fundamental to building trust and rapport within the team. Providing clear expectations and procedures, along with regular updates on project progress and challenges, creates a sense of shared responsibility and accountability. This transparency also allows for early identification and mitigation of potential roadblocks, ultimately leading to a more efficient and successful outcome.
Transparency in Decision-Making
Open communication extends beyond team dynamics to include decision-making processes. When decisions are made transparently, everyone understands the rationale behind them. This fosters greater buy-in and reduces the potential for misunderstandings or resentment. Clear communication of the factors considered and the reasoning behind a decision can significantly improve team morale and trust in leadership.
Clearly articulating the criteria for decision-making ensures fairness and consistency. This fosters a sense of equity and ensures that everyone feels valued and respected within the process. Furthermore, transparency in decision-making builds trust and confidence in the organization's leadership, leading to enhanced performance and productivity.
Building Trust through Open Communication
Open and honest communication is the cornerstone of trust. When team members feel comfortable expressing their ideas and concerns, they are more likely to collaborate effectively and take ownership of their work. Creating a safe space for open dialogue encourages a culture of psychological safety, where members feel comfortable sharing vulnerabilities and seeking help when needed.
Active listening and empathetic responses are vital components of open communication. Truly understanding different perspectives and acknowledging concerns are essential to fostering a collaborative and inclusive environment. By actively listening to and valuing the input of all team members, you build trust and rapport that are crucial for long-term success.
Accountability and Shared Responsibility
In a collaborative environment, clear roles and responsibilities are essential to ensure that everyone understands their part in achieving shared goals. Defining individual tasks and expectations upfront minimizes misunderstandings and ensures that everyone is accountable for their contributions. This also fosters a sense of ownership and motivation towards project completion.
Implementing regular check-ins and feedback mechanisms are vital for maintaining accountability. By tracking progress and providing constructive feedback, team members can identify areas for improvement and ensure that everyone is working towards the same objectives. This shared responsibility fosters a sense of collective effort and contributes to a higher level of project success.