Supply Chain Data Security: Protecting Your Most Valuable Digital Assets
The human element within supply chains remains a significant vulnerability. Social engineering tactics, such as phishing emails or fraudulent requests, can exploit employees at any level, from entry-level workers to senior management. These tactics can gain access to sensitive information or manipulate individuals into compromising security protocols. Combating this threat requires comprehensive security awareness training for all employees and robust authentication measures to prevent unauthorized access.
Furthermore, insider threats, whether intentional or unintentional, pose a serious risk. Malicious insiders with access to sensitive data or compromised employees acting on behalf of attackers can cause significant damage. Implementing strict access controls and regular security audits are vital to mitigate these risks.
IoT Integration and the Expanding Threat Landscape
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in manufacturing and logistics presents new security challenges. Connected devices, such as sensors and automated equipment, collect and transmit a wealth of data, creating a potential entry point for cybercriminals. Securing these devices and the data they transmit is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of the supply chain. Effective security measures need to be implemented at each stage of the supply chain, from initial device configuration to ongoing monitoring and maintenance.
The Importance of Collaboration and Shared Responsibility
Addressing the expanding attack surface requires a collaborative approach. Suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers must work together to implement and maintain robust security measures throughout the entire supply chain. Shared responsibility for security, including information sharing and joint risk assessments, is essential to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities effectively. Clear communication protocols and incident response plans must be established to ensure rapid and coordinated responses to security incidents.
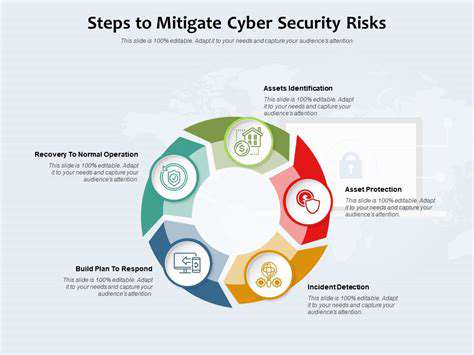
The Role of Secure Communication Channels and Data Encryption
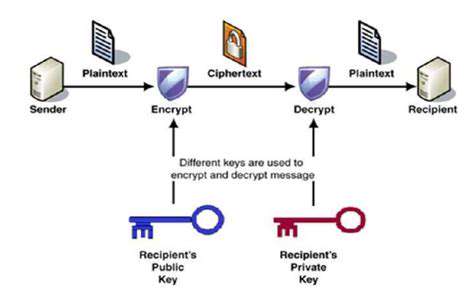
Importance of Secure Communication
Secure communication is paramount in today's interconnected world, encompassing a wide range of applications from online banking and e-commerce to confidential medical records and classified government information. Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and manipulation is crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring the integrity of transactions and information exchange. The consequences of a security breach can be devastating, ranging from financial losses and reputational damage to legal repercussions and even physical harm.
Implementing robust security measures is essential to mitigate the risks associated with insecure communication channels. These measures encompass a range of techniques, including encryption, authentication protocols, and access controls, all designed to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. By establishing secure communication channels, organizations and individuals can safeguard sensitive information and build a foundation of trust and reliability.
Types of Secure Communication Technologies
Various technologies are employed to ensure secure communication. One key method is encryption, which transforms data into an unreadable format before transmission, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to decipher the information. This method is vital for protecting data transmitted over public networks.
Another critical component is authentication, a process of verifying the identity of the sender or receiver to ensure that the communication originates from a legitimate source. Authentication protocols, such as digital signatures and certificates, play a crucial role in ensuring the authenticity of communications. These technologies are vital for safeguarding sensitive information, preventing fraudulent activities, and maintaining the integrity of digital interactions.
Furthermore, secure communication often involves the use of secure protocols, like HTTPS, which encrypts communication between a web browser and a website. These protocols are designed to protect data from eavesdropping and tampering.
Methods for Implementing Secure Communication
Implementing secure communication involves a multi-faceted approach. Organizations need to establish clear security policies and procedures that outline acceptable use, access controls, and incident response protocols. Employees should be trained on best practices for handling sensitive information and recognizing potential threats. This proactive approach helps to create a culture of security awareness and reduces the likelihood of security breaches.
Employing strong encryption algorithms is another crucial aspect of secure communication implementation. Organizations must choose encryption methods that provide adequate protection against the latest threats. This includes regularly updating software and hardware to ensure the implementation of the latest security patches. Regular security audits and penetration testing are also important to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Implementing secure communication requires a combination of technical solutions and organizational strategies. Strong security practices are vital to protecting sensitive data and maintaining trust in digital interactions.
The Future of Secure Communication
The future of secure communication is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in cryptography, networking, and artificial intelligence. New technologies are emerging, such as quantum cryptography, which promises unprecedented levels of security. These advancements will be crucial in addressing the growing complexity of cyber threats and the increasing volume of data being transmitted.
As technology continues to advance, securing communication will necessitate a constant adaptation and evolution of security protocols. Organizations and individuals need to stay informed about emerging threats and adopt new security measures to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of their communications.
A failing mass airflow sensor (MAF) often manifests as a noticeable drop in engine performance. You might experience sluggish acceleration, difficulty maintaining speed, and a general feeling of the engine struggling to respond to your commands. This decrease in power is a key indicator of a potential issue with the MAF sensor, as it's responsible for accurately measuring the airflow into the engine.
Implementing Robust Security Measures and Continuous Monitoring
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is crucial for bolstering security. MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide two or more verification methods before gaining access. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised. For instance, users might be prompted for a code sent to their mobile phone in addition to their password. This extra step makes it exponentially harder for attackers to gain access.
By enforcing MFA, organizations can significantly mitigate the threats posed by stolen credentials or phishing attacks. This proactive approach strengthens the overall security posture of the system, safeguarding sensitive data and preventing potential breaches.
Employing Strong Password Policies
Robust password policies are fundamental to a strong security framework. These policies should mandate the use of complex passwords, incorporating a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Enforcing a minimum password length also contributes to enhanced security. Password managers can help users create and store strong passwords securely, minimizing the risk of using weak or reused passwords across multiple accounts.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regular security audits and penetration testing are vital for identifying vulnerabilities in systems and applications. These assessments help organizations proactively address potential weaknesses before they are exploited by malicious actors. The process involves simulating real-world attacks to evaluate the effectiveness of existing security measures. A regular audit cycle is essential for staying ahead of evolving cyber threats and maintaining a strong security posture.
Penetration testing is a crucial part of this process, simulating attacks to identify vulnerabilities that automated scans might miss. The results of these tests can then be used to prioritize remediation efforts and strengthen the overall security infrastructure.
Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit
Data encryption, both at rest and in transit, is paramount for safeguarding sensitive information. Encrypting data stored on servers and databases protects it from unauthorized access in the event of a breach. Implementing encryption protocols for data transmission ensures that sensitive information remains confidential during its journey across networks. Robust encryption algorithms and key management practices are critical components of this strategy.
Regular Software Updates and Patching
Staying up-to-date with software updates and security patches is critical for maintaining a secure environment. Outdated software often contains known vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Implementing a system for automatic updates or regular manual patching can significantly reduce the risk of successful attacks. This proactive approach strengthens the security posture and minimizes the risk of exploitation.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Educating employees about security best practices is an essential component of a strong security program. Training programs should cover topics such as phishing awareness, safe password practices, and recognizing suspicious emails or links. Regular awareness campaigns can significantly reduce the risk of human error, a common vector for cyberattacks. Creating a security-conscious culture is crucial for long-term success.
Secure Network Configuration and Access Control
A secure network configuration is critical for preventing unauthorized access to systems and data. This involves implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control lists to restrict access to sensitive resources. Properly configured networks limit the attack surface and enhance the overall security posture. Regular review and adjustment of network configurations are essential to adapt to evolving threats.