ロボティックプロセスオートメーション(RPA)と物理ロボットの調和
The future of automation extends beyond the digital realm, integrating seamlessly with physical processes. This integration involves the use of robots and automated machinery to handle physical tasks, increasing productivity and safety in manufacturing, logistics, and warehousing. This convergence of digital and physical automation promises to revolutionize entire production lines, leading to improved output and reduced operational costs.
This integration is not merely about adding robots to existing processes; it's about designing entirely new systems that leverage both digital and physical automation for optimal performance. This approach allows for a more holistic and efficient approach to task completion, increasing overall output and reducing errors.
Enhanced Efficiency and Scalability
Automation, whether digital or physical, provides significant advantages in terms of efficiency and scalability. RPA, for example, can handle a large volume of tasks with high accuracy, freeing up human resources for more complex and strategic work. This allows businesses to handle increased workloads without requiring a proportional increase in human staff, leading to a significant return on investment.
The scalability aspect is particularly crucial in today's dynamic business environment. Automation allows businesses to easily adapt to changing demands by simply adjusting the workload assigned to the robotic processes. This flexibility is a major advantage over traditional methods that often struggle to keep pace with fluctuating operational needs.
Addressing Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While automation offers significant benefits, it's essential to acknowledge and address potential challenges. One key concern is the potential displacement of human workers. However, this transition can be managed through reskilling and upskilling programs, enabling employees to adapt to new roles and contribute to the automated workflow. This requires a proactive approach from businesses to ensure a smooth transition and minimize any negative impacts.
Ethical considerations regarding automation are also crucial. Ensuring data security and privacy, maintaining transparency in automated decision-making, and preventing bias in algorithms are vital concerns that need careful attention. A responsible approach to automation requires a thoughtful consideration of its potential impact on society and the development of ethical guidelines to ensure its beneficial application.
RPA: The Digital Workhorse

Understanding Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that automates business processes by using software robots. These robots, often referred to as bots, can perform repetitive tasks that are typically handled by humans, such as data entry, processing transactions, and interacting with various software applications. This automation can significantly improve efficiency and reduce errors, freeing up human workers for more strategic and creative tasks.
RPA is essentially a software-based solution that mimics human actions. It interacts with existing applications, systems, and data sources to carry out predefined tasks, streamlining workflows and improving overall operational performance.
Key Advantages of Implementing RPA
One significant advantage of RPA is improved efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks, businesses can reduce processing time and increase output. This results in faster turnaround times for customer requests and a greater overall throughput of work. It also helps streamline processes and enhance overall productivity.
Another key benefit is reduced errors. RPA bots perform tasks consistently and accurately, minimizing the chance of human error. This leads to higher data quality, greater accuracy in financial reporting, and fewer costly mistakes in operational processes. This reduction in errors also leads to better customer satisfaction.
RPA's Impact on Operational Efficiency
RPA's impact on operational efficiency is substantial. By automating tasks, businesses can free up human employees from tedious, time-consuming work, allowing them to focus on more strategic initiatives. This can translate to significant cost savings and a more productive workforce. It also enables faster response times to customer requests and a more responsive business environment.
Automation of repetitive tasks through RPA reduces the risk of errors and increases the accuracy of work done, which contributes to increased operational efficiency. RPA bots are programmed to execute tasks with precision and consistency.
RPA and Data Accuracy
Data accuracy is a critical component of any successful business operation. RPA systems are designed to interact with data sources and systems with a high degree of accuracy. This ensures that data is processed correctly and consistently, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies. This is particularly important in financial transactions, order processing, and other critical business functions.
Accurate data leads to informed decision-making and improved business performance. RPA significantly contributes to this by automating data entry and processing with high levels of precision, which reduces errors and ensures data integrity.
The Role of RPA in Customer Service
RPA can play a significant role in enhancing customer service by automating various aspects of the customer interaction process. This includes automating responses to frequently asked questions, processing orders, and providing real-time support. This leads to faster response times, improved customer satisfaction, and greater efficiency in handling customer inquiries.
By automating routine tasks, businesses can redirect human agents to more complex issues, leading to a more engaged and effective customer service team. This translates to better customer experiences and improved brand reputation.
Scaling RPA Solutions for Growth
As businesses grow, their operational needs also evolve. RPA solutions can be scaled to accommodate this growth, handling increasing volumes of work and expanding the scope of automation. This scalability is a crucial advantage in adapting to changing business demands and maintaining efficiency as the company expands.
RPA's scalability allows businesses to adapt to evolving needs without significant investment in new infrastructure or personnel. This adaptability is key to managing growth and maximizing the return on investment in RPA technology.
Future Trends in RPA
The field of RPA is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging regularly. One prominent trend is the integration of RPA with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). This integration enables bots to handle more complex tasks, learn from data, and adapt to changing circumstances.
Furthermore, the development of low-code and no-code RPA platforms is making it easier for businesses of all sizes to implement and manage automation solutions. This accessibility of advanced technology promises to drive wider adoption and further enhance the capabilities of RPA across various industries.
Physical Robotics: Bringing Automation to the Physical World

Hardware Components: The Foundation of Physical Robots
Physical robots, at their core, are complex machines requiring a robust physical structure. This structure, often referred to as the robot's hardware, comprises several critical components. These components must be meticulously designed and integrated for the robot to function effectively. From the mechanical frame providing support and movement to the actuators that provide power, each element plays a vital role in the robot's overall performance.
Key hardware elements include sensors, which allow the robot to perceive its environment, and actuators, the muscles of the robot, responsible for movement. These components are interconnected through intricate electrical and mechanical systems, forming a cohesive unit capable of carrying out complex tasks.
Software Control: Programming the Robot's Actions
The hardware of a physical robot is only half the story. To bring the robot to life, sophisticated software is needed to program its actions and behaviors. This software dictates how the robot interacts with its environment, how it responds to different inputs, and how it accomplishes its assigned tasks.
Programming a robot involves defining the logic and sequences that determine its actions. This can range from simple, pre-programmed tasks to complex algorithms that enable the robot to learn and adapt to changing situations. Advanced programming techniques, like machine learning and artificial intelligence, are increasingly used to create more intelligent and adaptable robots.
Sensory Perception: Enabling Environmental Awareness
A robot's ability to interact with its environment effectively hinges on its sensory perception capabilities. Sensors are essential for gathering information about the surroundings, allowing the robot to navigate, avoid obstacles, and perform tasks with precision. Different types of sensors are required to capture various aspects of the environment, such as light, sound, temperature, and pressure.
Vision systems are crucial for many robotic applications, allowing robots to see their surroundings and identify objects. Tactile sensors provide information about physical contact, enabling robots to manipulate objects with greater dexterity. These sensors, combined with sophisticated algorithms, empower robots to make informed decisions and respond appropriately to their surroundings.
Applications and Impact: Transforming Industries
Physical robots are transforming numerous industries, from manufacturing to healthcare to exploration. In manufacturing, robots automate repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency and reducing human error. They assist in assembling products, inspecting components, and performing other tasks requiring precision and speed.
In healthcare, robots are used for surgery, rehabilitation, and patient care. In exploration, robots can access hazardous or inaccessible environments, collecting data and performing tasks in dangerous or challenging situations. These applications highlight the adaptability and versatility of physical robots.
Future Directions: Advancements and Challenges
The field of physical robotics is constantly evolving, with new advancements pushing the boundaries of what robots can achieve. Researchers are working on developing more agile, intelligent, and adaptable robots. This includes improving sensor technology, enhancing communication protocols, and developing more sophisticated algorithms for decision-making.
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in areas such as cost-effectiveness, energy efficiency, and safety. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for widespread adoption and integration of physical robots into various aspects of daily life. Ensuring that these advancements are implemented responsibly and ethically is paramount to their positive impact on society.
Establishing a consistent daily routine is crucial for creating a predictable and supportive home environment. A predictable schedule reduces stress for everyone, allowing children to anticipate their day and know what to expect. This predictability fosters a sense of security and control, which in turn promotes positive behavior. Consider including time for learning, play, meals, and relaxation. Even seemingly small routines, such as a consistent bedtime routine, can have a significant impact on overall well-being and contribute to a calmer and more harmonious home atmosphere.
The Interplay of RPA and Physical Robotics
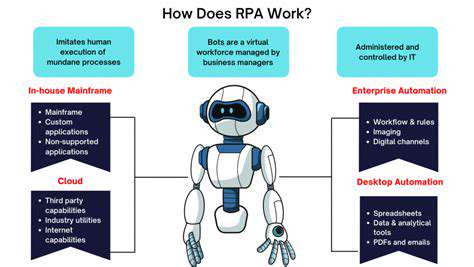
RPA's Impact on Efficiency
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is revolutionizing the way businesses operate by automating repetitive and rule-based tasks. This automation frees up human employees to focus on more complex and strategic work, leading to significant gains in operational efficiency. By automating mundane processes, RPA systems can significantly reduce processing time and improve accuracy, resulting in a notable increase in overall productivity. This increased efficiency translates to cost savings and allows businesses to scale operations more effectively.
Implementing RPA solutions can streamline workflows and reduce errors associated with manual data entry and processing. The consistent and reliable execution of tasks by RPA bots eliminates human error, leading to greater accuracy and reliability in the overall process. This is particularly beneficial in industries with stringent regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of costly mistakes.
The Physical Component in the Equation
While RPA excels at digital processes, the physical component often plays a crucial role in many business operations. Consider a warehouse environment, where order fulfillment requires both robotic process automation (RPA) and physical handling. RPA can manage order processing and inventory management digitally, while robots handle the physical movement of goods, creating a seamless and integrated operation.
Integrating RPA with physical processes is not just about automation; it's about creating a more robust and efficient system. This integration enhances productivity by optimizing the entire workflow, from the initial order to the final delivery. This synergy between virtual and physical operations enables businesses to respond more quickly to changing demands and market conditions.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the significant benefits, implementing RPA and integrating it with physical processes presents some challenges. Businesses must consider the potential need for significant infrastructure changes, such as upgrading existing hardware or software systems. Furthermore, employees may need training to adapt to new workflows and processes.
Another critical aspect involves cybersecurity. As RPA systems handle sensitive data, robust security measures are essential to protect against potential threats. Implementing secure data protocols and access controls is crucial to maintaining data integrity and preventing breaches.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of RPA and physical systems integration is promising, with ongoing innovations driving greater efficiency and collaboration. Expect to see more seamless integration between digital and physical processes, allowing for real-time data exchange and improved decision-making. Advanced machine learning and AI will further enhance the capabilities of RPA, enabling more complex and intelligent automation. This integration has the potential to reshape entire industries, leading to new levels of productivity and efficiency.
Furthermore, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) is creating new opportunities for integrating physical processes with RPA. The ability to connect and monitor physical assets in real-time allows for dynamic adjustments and optimized workflows, leading to better performance and reduced downtime.
Future Applications and Challenges
Expanding the Reach of RPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is no longer confined to simple, repetitive tasks. Future applications are poised to leverage RPA's adaptability to address increasingly complex business processes. This includes integrating RPA with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to automate decision-making, predict outcomes, and handle exceptions that previously required human intervention. The potential for RPA to significantly reduce operational costs and improve efficiency in sectors like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing is substantial. We're likely to see an evolution beyond simple data entry and transaction processing, towards more sophisticated tasks involving data analysis, reporting, and even customer interaction.
Furthermore, the integration of RPA with physical robots (physical robotics) opens up a new frontier. Imagine automated warehouses where physical robots, guided by RPA, can perform complex tasks like picking, packing, and shipping goods, significantly enhancing productivity and reducing labor costs. This convergence of digital and physical automation promises a future where businesses can achieve unprecedented levels of operational efficiency, allowing for greater focus on strategic initiatives. The potential for this fusion of technologies is truly transformative and will reshape entire industries.
Overcoming Hurdles and Ethical Considerations
While the potential of RPA and physical robotics is vast, significant challenges remain. Ensuring data security and privacy in increasingly automated environments is paramount. Robust security measures are crucial to prevent unauthorized access and manipulation of sensitive data. The ethical implications of widespread automation, particularly concerning job displacement, need careful consideration. Strategies for reskilling and upskilling the workforce to adapt to the changing job market need to be developed and implemented proactively.
Another crucial challenge is the integration of RPA systems with existing legacy systems. Frequently, businesses rely on a complex web of disparate systems, making seamless integration a significant hurdle. Developing adaptable and flexible RPA platforms that can interact with various systems is critical for successful implementation. Addressing this challenge will be key to widespread adoption and realizing the full potential of this technology.
The integration of RPA with physical robots also raises questions about the reliability and maintenance of these complex systems. Ensuring the consistent performance and uptime of both the software and hardware components is essential. Efficient maintenance strategies and robust troubleshooting protocols will be critical for smooth operation and minimizing downtime.
Finally, the ongoing development of sophisticated algorithms and AI models to drive RPA capabilities will continue to be crucial. Addressing the need for ongoing training and updating of these systems is essential to keep them aligned with evolving business needs. Further research and development in this area are essential for the continued advancement of the technology.
The future of RPA and physical robotics depends on our ability to address these challenges proactively. By working together to develop secure, ethical, and adaptable solutions, we can unlock the full potential of these technologies and create a more efficient and productive future.